基于js的数据结构
# 一、前沿
# 亮点:
1、思维导图
2、js实现
3、参考资料
4、思维导图里面的算法可视化网站
# 二、思维导图
三个思维导图:前面两个是什么语言都是通用的,第三个是基于js的,可以结合前面两个和js语言特点来实现。
这三个思维导图还是挺有保存意义的
# 计算机数据结构思维导图
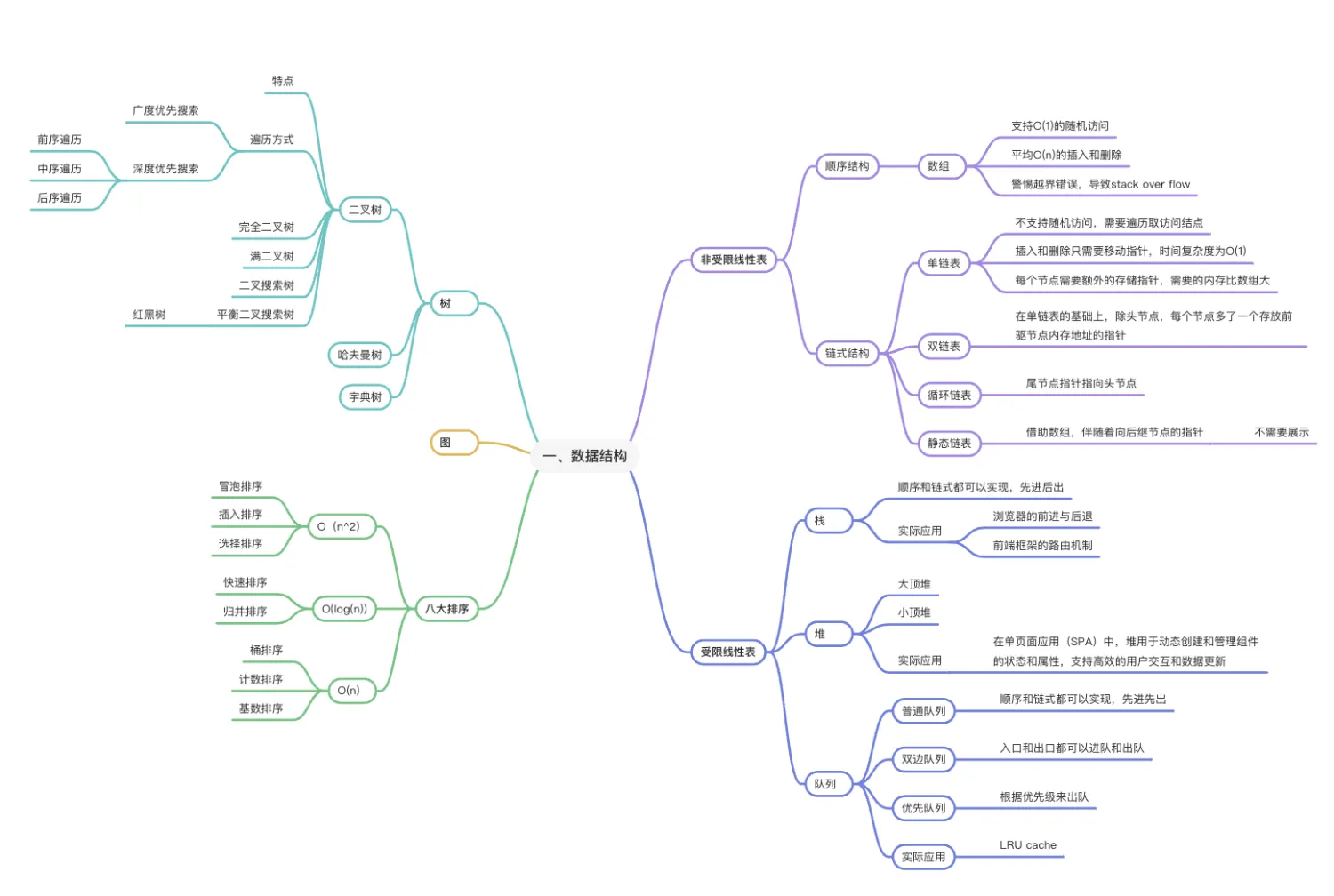
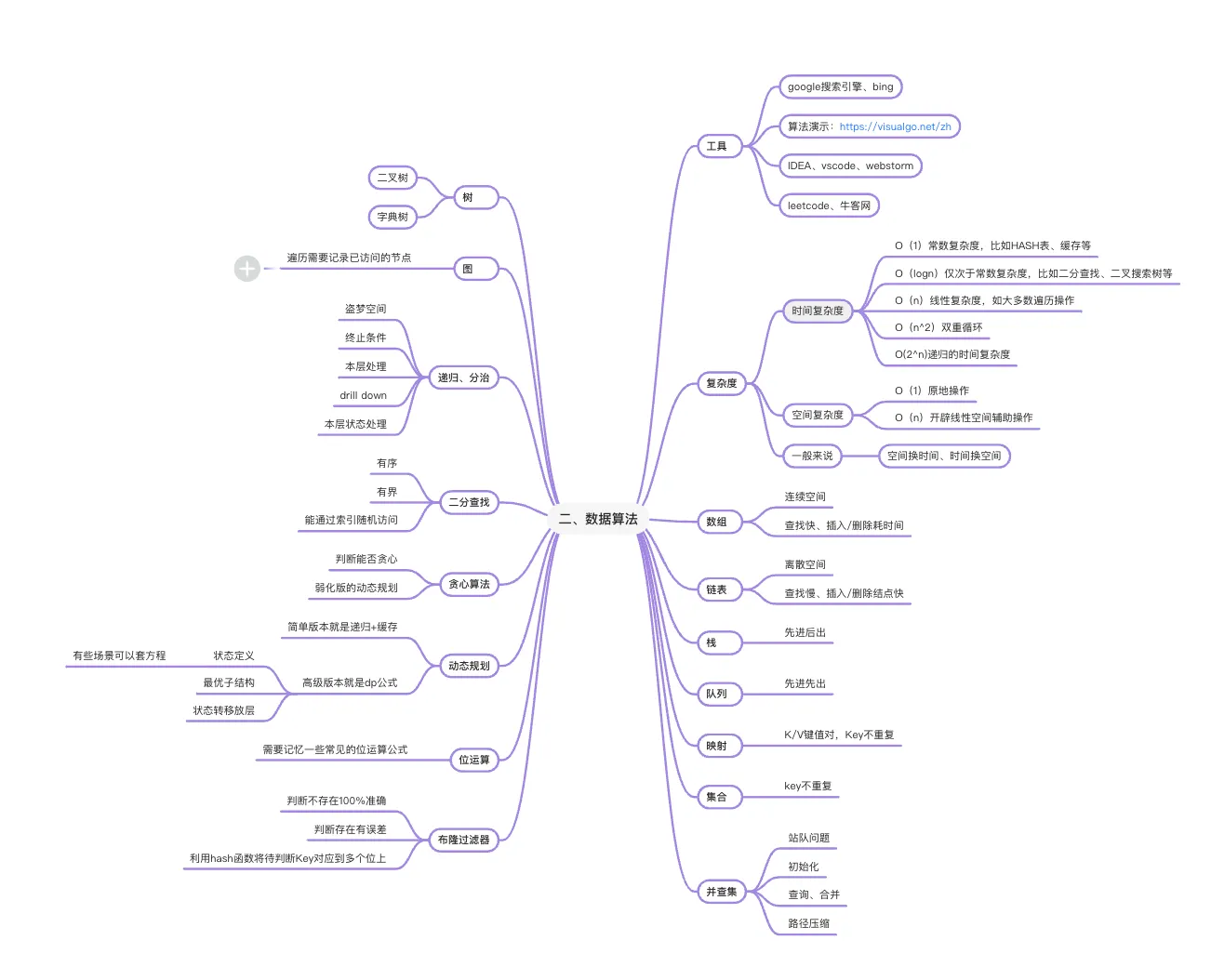
# 计算机算法思维导图
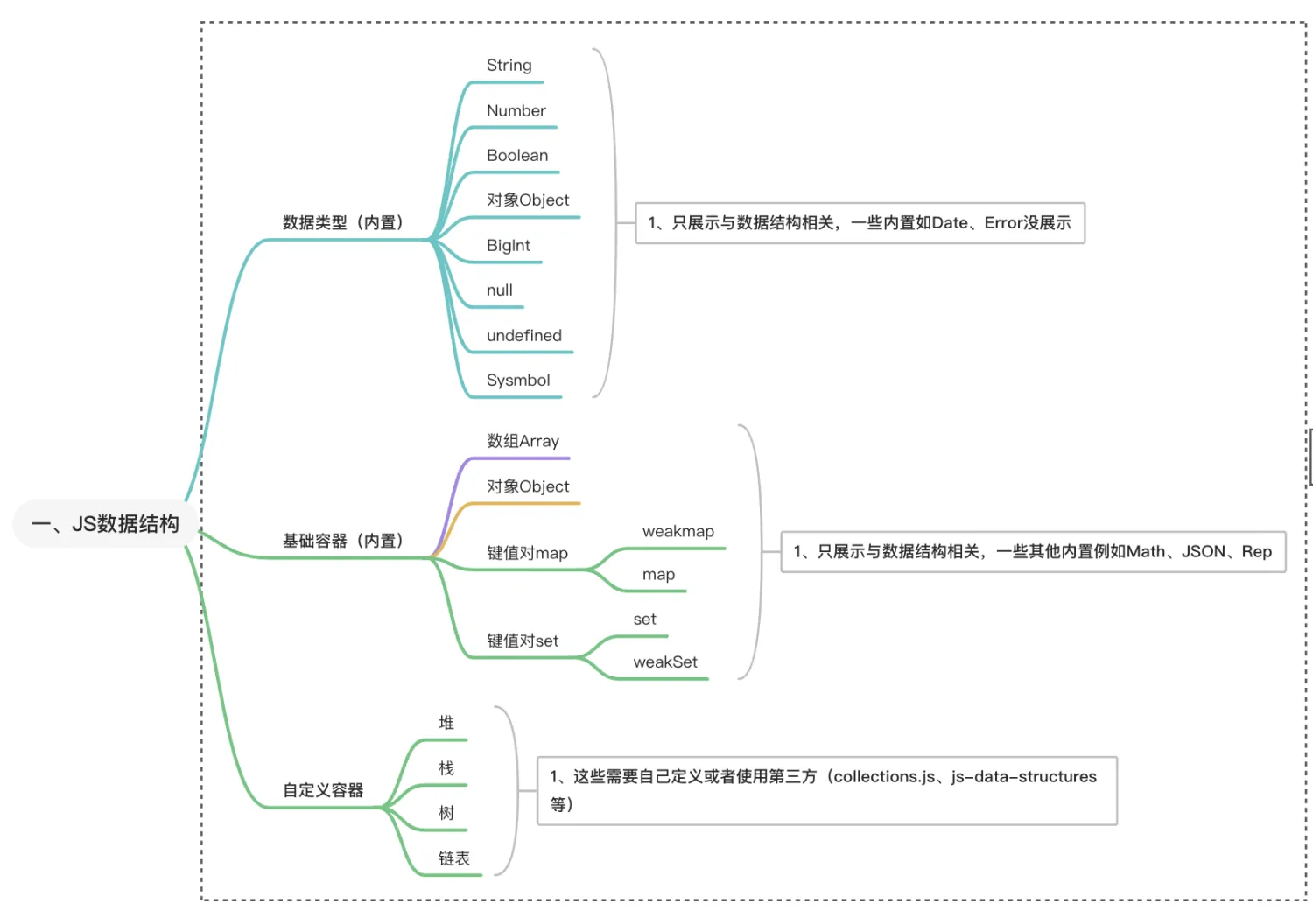
# JS数据结构
# 二、概要
先要了解数据结构,在了解算法,然后是相辅相成。因为有些算法是基于数据结构来实现的
js的数据结构有自己的特点,而且内置api有JSON这种与数据结构相关的
# 三、数据结构
# 3.1、非受限数据结构
这个主要是说一些不受条件限制的一些数据结构比如:数组、链表,关于数组,js有提供专门的容器比如Array,但是链表来说,需要自己定义或者第三方
# 数组array
描述
- 主要分为一维数组、二维数组,多维数组
- 优点:随机访问:可以通过索引在 O(1) 时间内快速访问任何元素;内存效率:所有元素存储在连续的内存位置,访问速度较快。
- 缺点:a插入和删除效率低:在数组中间插入或删除元素时,可能需要移动大量元素,时间复杂度为 O(n)。b固定大小:一旦创建,数组的大小通常是固定的,无法动态扩展。
关于缺点
主要是js内置了array,扩展数组长度能够看起来无感,其实看源代码,比如java的数组,他的实现ArrayList,里面的对push操作有判断,需要如果超过了就需要分配空间,但是对于js来说可以不固定。
基于js的操作
具体可以看说明书:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
- 添加元素
arr.push(4); // arr 变为 [1, 2, 3, 4]
arr.unshift(0); // arr 变为 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
- 删除元素
const last = arr.pop(); // last 是 4, arr 变为 [0, 1, 2, 3]
const first = arr.shift(); // first 是 0, arr 变为 [1, 2, 3]
- 访问元素
const firstElement = arr[0]; // 访问第一个元素
arr[1] = 5; // 修改第二个元素
- 遍历元素
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { console.log(arr[i]); }
arr.forEach((element) => { console.log(element); });
- 数组操作
const newArr = arr.slice(1, 3); // 返回 [2, 3]
arr.splice(1, 1, 10); // 从索引1开始删除1个元素并添加10,arr 变为 [1, 10, 3]
- 查找
const index = arr.indexOf(10); // 返回 1
const hasTen = arr.includes(10); // 返回 true
- 数组反转与排序
arr.sort(); // 默认按字符串Unicode顺序排序
arr.reverse(); // arr 反转
- 合并数组
const arr1 = [1, 2];
const arr2 = [3, 4];
const combined = arr1.concat(arr2); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
- 转化数组
const str = arr.join('-'); // '1-10-3'
使用场景
- 存列表数据
- 排序和过滤
- 实现队列、栈
# 链表link
具体讲解链表需要单独开文章(TODO)
描述
- 链表也有多种:单链表、双链表、循环链表
js(单链表)实现
// 1、新建节点类(Node)
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data; // 节点数据
this.next = null; // 指向下一个节点的引用
}
}
// 2、新建链表类(LinkedList)
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null; // 链表的头节点
this.size = 0; // 链表的大小
}
// 添加节点到链表末尾
append(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode; // 如果链表为空,头节点指向新节点
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到链表末尾
}
current.next = newNode; // 将新节点添加到末尾
}
this.size++; // 增加链表大小
}
// 插入节点到指定位置
insert(data, index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
return; // 索引无效
}
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (index === 0) {
newNode.next = this.head; // 头插
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
let previous;
let count = 0;
while (count < index) {
previous = current; // 记录前一个节点
current = current.next;
count++;
}
newNode.next = current; // 新节点指向当前节点
previous.next = newNode; // 前一个节点指向新节点
}
this.size++;
}
// 删除指定位置的节点
remove(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
return; // 索引无效
}
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next; // 删除头节点
} else {
let previous;
let count = 0;
while (count < index) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
count++;
}
previous.next = current.next; // 前一个节点跳过当前节点
}
this.size--;
}
// 打印链表
print() {
let current = this.head;
const elements = [];
while (current) {
elements.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
console.log(elements.join(' -> '));
}
}
// 3、使用
const list = new LinkedList();
list.append(10);
list.append(20);
list.append(30);
list.print(); // 输出: 10 -> 20 -> 30
list.insert(15, 1);
list.print(); // 输出: 10 -> 15 -> 20 -> 30
list.remove(2);
list.print(); // 输出: 10 -> 15 -> 30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
使用场景
- 动态大小的数据存储
- 实现队列和栈
- 特定算法的实现(某些算法(如链表排序、合并两个有序链表)直接使用单链表作为基础数据结构,以提高效率。)
- 多线程或异步处理(在需要处理任务队列的多线程或异步环境中,单链表可以用于维护任务的顺序,确保按顺序处理。)
- 图形和游戏开发
# 3.2、受限数据结构
受限的比如栈、队列、堆,但是js没有内置提供专门的api、属性,所以需要自己实现或者第三方
# 栈stack
描述
- 栈的一般限制是先进后出
js实现:
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.items = []; // 存储栈的元素
}
// 入栈
push(element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
// 出栈
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null; // 栈为空,返回null
}
return this.items.pop();
}
// 查看栈顶元素
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null; // 栈为空,返回null
}
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
// 检查栈是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
// 返回栈的大小
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
// 打印栈
print() {
console.log(this.items.join(' '));
}
}
// 使用示例
const stack = new Stack();
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(30);
stack.print(); // 输出: 10 20 30
console.log(stack.pop()); // 输出: 30
console.log(stack.peek()); // 输出: 20
stack.print(); // 输出: 10 20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
基本操作
- 入栈(Push):将元素添加到栈的顶部。
- 出栈(Pop):移除并返回栈顶部的元素。
- 查看栈顶元素(Peek):返回栈顶部的元素,但不移除它。
- 检查栈是否为空(IsEmpty):判断栈中是否还有元素。
常用场景:
- 函数调用管理
- 撤销功能
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)
- 状态管理
# 队列queue
描述
- 队列来说一般是先进先出
- 队列来说是单端队列,也可以双端队列
js实现双端队列:
class Deque {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
// 从队尾插入元素
enqueueBack(element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
// 从队首插入元素
enqueueFront(element) {
this.items.unshift(element);
}
// 从队首移除元素
dequeueFront() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null; // 或者抛出错误
}
return this.items.shift();
}
// 从队尾移除元素
dequeueBack() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null; // 或者抛出错误
}
return this.items.pop();
}
// 查看队首元素
front() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null; // 或者抛出错误
}
return this.items[0];
}
// 查看队尾元素
back() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null; // 或者抛出错误
}
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
// 检查双端队列是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
// 获取双端队列的大小
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
// 清空双端队列
clear() {
this.items = [];
}
}
// 使用示例
const deque = new Deque();
deque.enqueueBack(1);
deque.enqueueBack(2);
deque.enqueueFront(0);
console.log(deque.front()); // 输出: 0
console.log(deque.back()); // 输出: 2
console.log(deque.dequeueFront()); // 输出: 0
console.log(deque.dequeueBack()); // 输出: 2
console.log(deque.size()); // 输出: 1
console.log(deque.isEmpty()); // 输出: false
deque.clear();
console.log(deque.isEmpty()); // 输出: true
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
操作:
- enqueueBack:在队尾插入元素。
- enqueueFront:在队首插入元素。
- dequeueFront:从队首移除并返回元素。
- dequeueBack:从队尾移除并返回元素。
- front:查看队首元素但不移除。
- back:查看队尾元素但不移除。
- isEmpty:检查双端队列是否为空。
- size:返回双端队列中元素的数量。
- clear:清空双端队列。
常用场景:
- 任务调度:在需要优先处理的任务和普通任务之间进行高效管理时,可以将优先任务插入队首,普通任务插入队尾。
- 缓存实现:如 LRU(最近最少使用)缓存策略,可以使用双端队列来快速地将最近使用的项移动到队首,过期的项可以从队尾移除。
- 回溯算法:在深度优先搜索(DFS)或某些图形遍历中,可以使用双端队列来存储路径,从而能够在遍历过程中灵活地添加和删除节点。
- 字符串处理:在需要频繁地从两端添加或删除字符的场景中,比如回文判断,可以使用双端队列来高效管理字符串的状态。
- 消息队列:在实时系统或网络服务中,双端队列可以用来实现生产者-消费者模式,允许生产者在两端添加消息,消费者则可以从任意一端取出消息。
- 滑动窗口问题:在处理需要跟踪数据流的滑动窗口问题时,双端队列可以有效维护当前窗口的状态,支持快速插入和删除。
# 堆heap
描述
- 堆是一种特殊的树形数据结构。更具体地说,堆是一种完全二叉树
- 堆是一个完全二叉树,这意味着除了最后一层外,每一层都是完全填满的,最后一层的节点都在左侧
- 堆可以是最大堆或最小堆(最大堆:每个节点的值都大于或等于其子节点的值,最小堆:每个节点的值都小于或等于其子节点的值。)
js的最小堆实现
下面是通过数组array实现的,根据链表的还没实现
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
// 获取父节点索引
getParentIndex(index) {
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
// 获取左子节点索引
getLeftChildIndex(index) {
return index * 2 + 1;
}
// 获取右子节点索引
getRightChildIndex(index) {
return index * 2 + 2;
}
// 交换两个元素
swap(index1, index2) {
[this.heap[index1], this.heap[index2]] = [this.heap[index2], this.heap[index1]];
}
// 向堆中插入元素
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
this.bubbleUp();
}
// 上浮操作
bubbleUp() {
let index = this.heap.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
if (this.heap[index] >= this.heap[parentIndex]) break;
this.swap(index, parentIndex);
index = parentIndex;
}
}
// 从堆中删除最小元素
extractMin() {
if (this.heap.length === 0) return null;
if (this.heap.length === 1) return this.heap.pop();
const min = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
this.bubbleDown();
return min;
}
// 下沉操作
bubbleDown() {
let index = 0;
const length = this.heap.length;
while (true) {
const leftChildIndex = this.getLeftChildIndex(index);
const rightChildIndex = this.getRightChildIndex(index);
let smallestIndex = index;
if (leftChildIndex < length && this.heap[leftChildIndex] < this.heap[smallestIndex]) {
smallestIndex = leftChildIndex;
}
if (rightChildIndex < length && this.heap[rightChildIndex] < this.heap[smallestIndex]) {
smallestIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
if (smallestIndex === index) break;
this.swap(index, smallestIndex);
index = smallestIndex;
}
}
// 获取最小元素但不移除
peek() {
return this.heap[0] || null;
}
// 获取堆的大小
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
// 检查堆是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
}
// 使用示例
const minHeap = new MinHeap();
minHeap.insert(10);
minHeap.insert(5);
minHeap.insert(3);
minHeap.insert(8);
console.log(minHeap.peek()); // 输出: 3
console.log(minHeap.extractMin()); // 输出: 3
console.log(minHeap.peek()); // 输出: 5
console.log(minHeap.size()); // 输出: 3
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
常用场景
堆通常用于实现优先队列,支持高效的插入和删除最大(或最小)元素操作。虽然堆通常用数组实现,但其结构本质上是树形的。
# 3.3、树
主要讲二叉树、哈夫曼树、字典树
1、树是一种逻辑结构,所以基于js能用array、linkList实现,其他语言如java,也可以用ArrayList、linkList实现等
# 3.3.1、普通二叉树(Binary Tree)
- 定义:普通二叉树是一个每个节点最多有两个子节点的树结构,没有其他特定的约束。
- 特点:节点的分布没有限制,可以是任何形状。
# 3.3.2、满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)
- 定义:每个非叶子节点都有两个子节点,且所有的叶子节点在同一层上。
- 特点:结构非常规则,所有节点都被完全填满。
- 关系:满二叉树是普通二叉树的一种特例。
- 解释:如何最后子节点没满,就不是满二叉树
# 3.3.3、 完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)
- 定义:除了最后一层外,每一层都被完全填满,最后一层的节点必须从左到右填充。
- 特点:最后一层可以不满,但节点填充是左对齐的。
- 关系:完全二叉树也是普通二叉树的一种特例,但它比满二叉树更宽松,因为最后一层可以不满。
js实现:
class TreeNode {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class CompleteBinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
this.nodes = []; // 用于保持插入顺序,支持完全二叉树结构
}
insert(value) {
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
this.nodes.push(newNode); // 将节点添加到数组中
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode; // 如果树为空,则新节点为根节点
} else {
// 找到父节点
const index = this.nodes.length - 1;
const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
const parentNode = this.nodes[parentIndex];
if (index % 2 === 1) {
parentNode.left = newNode; // 左子节点
} else {
parentNode.right = newNode; // 右子节点
}
}
}
inOrderTraversal(node = this.root) {
if (node) {
this.inOrderTraversal(node.left);
console.log(node.value);
this.inOrderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
preOrderTraversal(node = this.root) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraversal(node.left);
this.preOrderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
postOrderTraversal(node = this.root) {
if (node) {
this.postOrderTraversal(node.left);
this.postOrderTraversal(node.right);
console.log(node.value);
}
}
}
// 使用示例
const tree = new CompleteBinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(5);
tree.insert(15);
tree.insert(3);
tree.insert(7);
tree.insert(12);
tree.insert(18);
console.log("In-order traversal:");
tree.inOrderTraversal(); // 应该按照排序顺序输出
console.log("Pre-order traversal:");
tree.preOrderTraversal();
console.log("Post-order traversal:");
tree.postOrderTraversal();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
# 3.3.4. 二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, BST)
- 定义:一种特殊的二叉树,满足以下条件:对于每个节点,左子树的所有节点的值都小于该节点的值,右子树的所有节点的值都大于该节点的值。
- 特点:二叉搜索树并不要求每个节点都有两个子节点,也没有层数的限制,但它必须满足排序的性质。
- 关系:二叉搜索树是一种特殊的普通二叉树,但不一定是满二叉树或完全二叉树。
js实现:
class TreeNode {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(value) {
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode; // 如果树为空,设定新节点为根节点
} else {
this._insertNode(this.root, newNode); // 从根节点开始插入
}
}
_insertNode(node, newNode) {
if (newNode.value < node.value) {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = newNode; // 左子树为空,插入新节点
} else {
this._insertNode(node.left, newNode); // 递归插入左子树
}
} else {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode; // 右子树为空,插入新节点
} else {
this._insertNode(node.right, newNode); // 递归插入右子树
}
}
}
find(value) {
return this._findNode(this.root, value);
}
_findNode(node, value) {
if (node === null) return false; // 节点为空,未找到
if (value === node.value) return true; // 找到节点
return value < node.value
? this._findNode(node.left, value) // 递归查找左子树
: this._findNode(node.right, value); // 递归查找右子树
}
inOrderTraversal(node = this.root) {
if (node) {
this.inOrderTraversal(node.left);
console.log(node.value);
this.inOrderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
}
// 使用示例
const bst = new BinarySearchTree();
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(15);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(12);
bst.insert(18);
console.log("In-order traversal:");
bst.inOrderTraversal(); // 按升序输出
console.log("Find 7:", bst.find(7)); // 输出 true
console.log("Find 20:", bst.find(20)); // 输出 false
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
# 3.3.5、总结关系
- 普通二叉树 是一个广泛的概念,包含所有类型的二叉树。
- 满二叉树 和 完全二叉树 都是普通二叉树的特例,但有各自的结构要求。
- 二叉搜索树 也是普通二叉树的一种,强调了节点的值的排序特性,而不强调节点的数量或层数的完整性。
# 3.4、图
图接触不是很多,所以很难解释得清楚
# 3.5、其他
# 3.5.1、set
关于set主要是js的es6推出的,主要关注set与weakSet的区别、
记住set里面的数据是不可重复的,所以也能做去重操作
js使用
const mySet = new Set();
mySet.add(1);
mySet.add({ name: 'Alice' });
console.log(mySet); // Set(2) { 1, { name: 'Alice' } }
2
3
4
# 3.5.2、map
# 四、算法
专门独立一章《基于js的算法入门》
# 参考资料
1、https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37255976/article/details/134464573
2、https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Data_structures
